BankAccount Problem(은행계좌 문제)
세마포를 사용해 해결할 수 있는 문제는 Mutual exclusion(상호 배타)와 Ordering(순서를 어떻게할지) 이다.
다음 예제 코드를 통해 위 문제에 대한 세마포의 활용방법을 알아보자.
1. Mutual exclusion(상호 배타) : 한번에 한 쓰레드만 접근하도록
부모님은 은행 계좌에 입금; 자녀는 출금하는 예제이다.
Thread를 상속받은 Parent와 Child 클래스를 만들어 BankAccount에 각각 입금, 출금을 반복해본다.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount b = new BankAccount();
Parent p = new Parent(b);
Child c = new Child(b);
p.start();
c.start();
p.join(); //쓰레드가 끝날때까지 기다린다.
c.join();
System.out.println("\nbalance = " + b.getBalance());
}
}
class BankAccount {
int balance;
void deposit(int amount) {
//임시변수인 temp에 저장하는 이유는 일부러 시간지연을 일으키기 위해서이다.
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+"); //입금 시 +를 출력한다.
balance = temp;
}
void withdraw(int amount) {
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-"); //출금 시 -를 출력한다.
balance = temp;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
class Parent extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Parent(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
b.deposit(1000);
}
}
}
class Child extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Child(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
b.withdraw(1000);
}
}
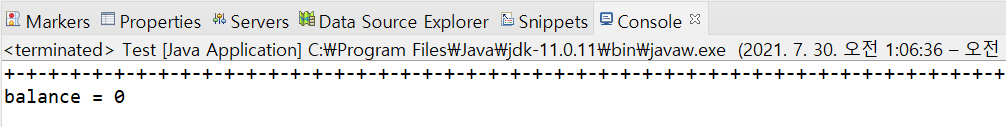
}출력 결과
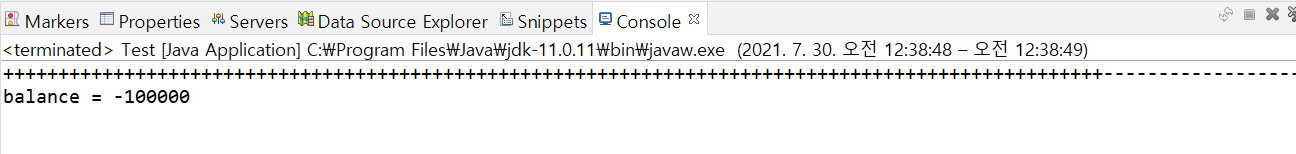
1) 문제점
잔액이 0원이 아니라 잘못된 값이 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
공통 변수인 balance에 두개의 쓰레드가 동시에 접근했기 때문이다.(=임계구역 문제)
2) 해결책
이와 같은 문제는 공통 변수에 한번에 한 쓰레드만 업데이트하도록 처리함으로써 해결할 수 있다.
Critical section(=임계구역)인 입금, 출금을 하기 전에 세마포를 만들었다. (sem.acquire(), sem.release)
sem = new Semephore(1) 로 생성자를 만들어 1개의 쓰레드만 동시접근 가능하도록 만든다.
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
//...
//생략
//...
class BankAccount {
int balance;
Semaphore sem;
BankAccount() {
sem = new Semaphore(1); //Semaphore(int n)은 n개의 쓰레드만큼 동시 접근을 허용한다는 의미이다.
}
void deposit(int amount) {
try {
sem.acquire(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에 잡아둔다.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
sem.release(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에서 빠져나오게 만든다.
}
void withdraw(int amount) {
try {
sem.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
sem.release();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
//...
//생략
//...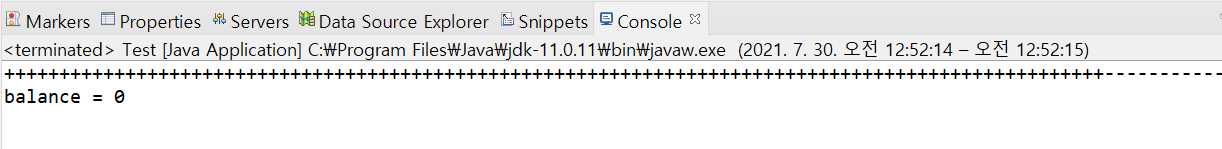
정상적인 결과값이 출력되는 것을 알 수 있다.
2. Ordering : 내가 원하는 순서대로 공통 변수에 접근하도록
1) 항상 입금 먼저(=Parent 먼저)
만약 항상 입금(+)이 출금(-) 보다 먼저 나오도록 만드려면 어떻게 해야할까?
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
//...
//생략
//...
class BankAccount {
int balance;
Semaphore sem, sem2;
BankAccount() {
sem = new Semaphore(1);
sem2 = new Semaphore(0);
}
void deposit(int amount) {
try {
sem.acquire(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에 잡아둔다.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
sem.release(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에서 빠져나오게 만든다.
sem2.release();
}
void withdraw(int amount) {
try {
sem2.acquire();
sem.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
sem.release();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
//...
//생략
//...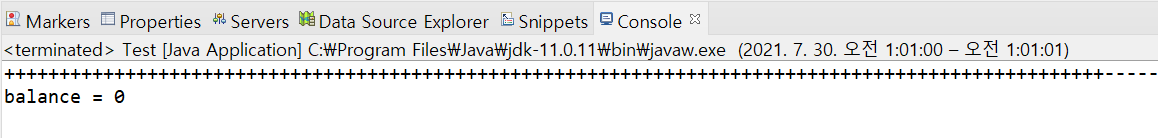
몇 번을 실행해봐도 입금(+)이 먼저 나오는 것을 알 수 있다.
2) 항상 출금 먼저(=Child 먼저)
만약 항상 출금(-)이 입금(+)보다 먼저 나오도록 만드려면 어떻게 해야할까?
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
//...
//생략
//...
class BankAccount {
int balance;
Semaphore sem, sem2;
BankAccount() {
sem = new Semaphore(1);
sem2 = new Semaphore(0);
}
void deposit(int amount) {
try {
sem2.acquire();
sem.acquire(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에 잡아둔다.
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
sem.release(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에서 빠져나오게 만든다.
}
void withdraw(int amount) {
try {
sem.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
sem.release();
sem2.release();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
//...
//생략
//...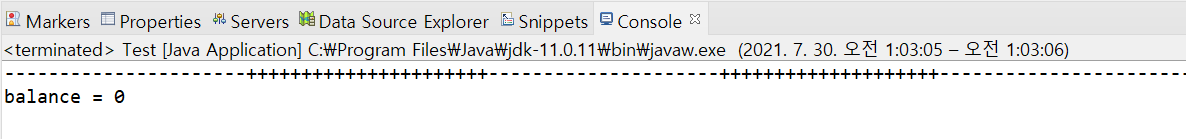
몇 번을 실행해봐도 출금(-)이 먼저 나오는 것을 알 수 있다.
3) 입출금 교대로(P-C-P-C-P-C-...)
만약 입금(+)과 출금(-)이 번갈아 나오도록 하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
//...
//생략
//...
class BankAccount {
int balance;
Semaphore sem, dsem, wsem;
BankAccount() {
sem = new Semaphore(1);
dsem = new Semaphore(0);
wsem = new Semaphore(0);
}
void deposit(int amount) {
try {
sem.acquire(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에 잡아둔다.
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
sem.release(); //쓰레드를 세마포 내부 큐에서 빠져나오게 만든다.
wsem.release();
dsem.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
void withdraw(int amount) {
try {
wsem.acquire();
sem.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
sem.release();
dsem.release();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
//...
//생략
//...
항상 입금(+)과 출금(-)이 번갈아 나오는 것을 알 수 있다.
'Programming > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 전통적 동기화 예제 (2) 공유 데이터베이스 접근 (0) | 2021.08.27 |
|---|---|
| 전통적 동기화 예제 (1) 생산자 - 소비자 문제 (0) | 2021.08.25 |
| 프로세스 동기화 도구 - 세마포 (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| 프로세스 동기화 (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| 프로세스 동기화 (0) | 2021.07.28 |
